Technical Highlights
Manufacturer: CNH Industrial (Case & New Holland)
Engine Family: FPT NEF Tier 4a Diesel Engines
Document Type: Factory Emission System Presentation
Date: September 2013
Slides: 46
System Type: Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) using Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF / AdBlue)
Emission Compliance: Tier 4a (Interim) and Tier 4b (Final) for off-road diesel engines
Coverage
Introduction to Tier 4 Regulations
EPA emission standards and phasing (Tier 1–4b)
90% reduction in PM and NOx required for Tier 4b
Comparison of CO, HC, NOx, and PM limits across engine power ranges
Pollutant Formation and Control
Chemistry of NOx and PM generation during diesel combustion
Relationship between temperature and NOx emissions
Acid rain and health effects from PM inhalation
Emission Solutions for Tier 4
Comparison: SCR vs CEGR/DPF (Exhaust Gas Recirculation with Diesel Particulate Filter)
Advantages of SCR on 850M–2050M dozers (fuel efficiency, less maintenance)
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) Overview
5% fuel savings through high-efficiency combustion
Conversion of NOx to nitrogen (N₂) and water (H₂O) by DEF injection
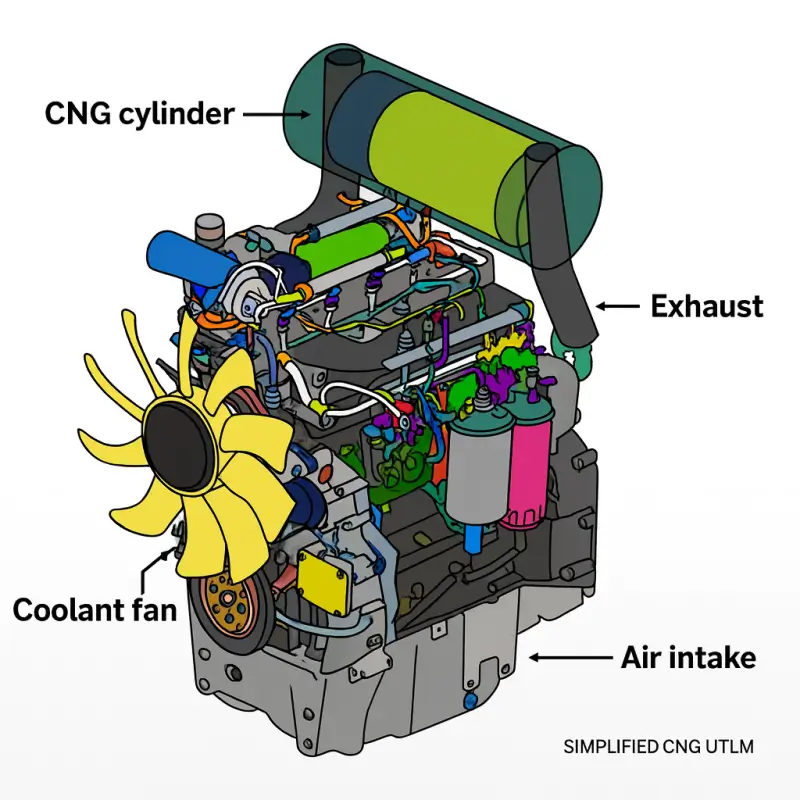
Core components: DEF tank, supply module, injector, mixing baffle, and catalyst
Component Layout and Hydraulic Scheme
Diagram showing DEF flow circuit between DCU (Dosing Control Unit), Supply Module, and Injector
Pressure range: 5 bar at dosing module (Bosch SM)
Sensors: NOx, temperature (upstream/downstream), DEF level, and humidity
DEF (AdBlue) System and WEMA Tank Module
32.5% urea / 67.5% distilled water composition
Freezing point −11°C; includes coolant-heated WEMA probe
Magnetic fill neck prevents misfuelling and ensures expansion space
DEF Injector and Mixer Assembly
Bosch dosing valve (200 g/h to 9 kg/h)
Active cooling and 54° spray angle
Mixer ensures proper DEF vaporization before catalyst
Filtration and Maintenance Intervals
Inline pre-filter (100 µm Voss) – clean/replace every 600–1200 hrs
Main filter – replace every 1200 hrs
Injector filter – no maintenance required
System Logic and DNOx Function Sequence
Pressure build-up → Reverting valve check → Normal dosing → Afterrun purge
Afterrun (90 seconds): reverses flow to clear DEF lines
Electronics and Diagnostics
ECU & DCU control with 5 sensors and 2 actuators
EST (Electronic Service Tool) and EASY software integration
Urea Dosing System Test (UDST) for performance validation
Faults, Inducements & Tamper Protection
DEF low level, poor quality, SCR failure triggers performance limits
Anti-tamper algorithm prevents software downgrades
Severe inducement = 50% torque reduction + RPM limitation
Delivery
The download link will be sent to your email instantly after payment.




 Abrites AVDI J2534
Abrites AVDI J2534 Actia Multi-Diag
Actia Multi-Diag Autoland iSCAN
Autoland iSCAN Bobcat Diagnostic Kit
Bobcat Diagnostic Kit BMW ENET
BMW ENET Bosch Mastertech II J2534
Bosch Mastertech II J2534 Bosch MTS 6531
Bosch MTS 6531 CAN CLIP RLT2002
CAN CLIP RLT2002 CarDAQ-Plus 3
CarDAQ-Plus 3 Cummins INLINE Datalink
Cummins INLINE Datalink Dearborn Protocol Adapter (DPA) 5
Dearborn Protocol Adapter (DPA) 5 Delphi/Autocom DS150E
Delphi/Autocom DS150E DrewLinQ
DrewLinQ Volvo VIDA DiCE
Volvo VIDA DiCE Derelek USB DIAG 3
Derelek USB DIAG 3 Electronic Data Link (EDL) 2
Electronic Data Link (EDL) 2 Electronic Data Link (EDL) 3
Electronic Data Link (EDL) 3 GM MDI 1
GM MDI 1 GM MDI 2
GM MDI 2 HEX-V2 VCDS VAG-COM
HEX-V2 VCDS VAG-COM Isuzu IDSS IDS MX1
Isuzu IDSS IDS MX1 Isuzu IDSS IDS MX2
Isuzu IDSS IDS MX2 Iveco Eltrac E.A.SY. ECI
Iveco Eltrac E.A.SY. ECI MaxiFlash Elite J2534
MaxiFlash Elite J2534 MB Star C6
MB Star C6 Mongoose J2534
Mongoose J2534 Nexiq USB-Link 1
Nexiq USB-Link 1 Nexiq USB-Link 2
Nexiq USB-Link 2 Nexiq USB-Link 3
Nexiq USB-Link 3 Noregon DLA+ 2.0
Noregon DLA+ 2.0 Porsche PIWIS TESTER 3 (PT3G)
Porsche PIWIS TESTER 3 (PT3G) PSA LEXIA 3
PSA LEXIA 3 SAE J2434
SAE J2434 Scania VCI 3
Scania VCI 3 Scanmatik 2 PRO
Scanmatik 2 PRO SD Connect Multiplexer
SD Connect Multiplexer Tactrix OpenPort 2.0
Tactrix OpenPort 2.0 Toyota TIS Mini VCI
Toyota TIS Mini VCI VAG ODIS VAS5054 Clone
VAG ODIS VAS5054 Clone VAG ODIS VAS6154 Clone
VAG ODIS VAS6154 Clone Volvo VOCOM 1
Volvo VOCOM 1 Volvo VOCOM 2
Volvo VOCOM 2 Xentry VCI
Xentry VCI Yanmar Diagnostic Interface Box (IFBOX)
Yanmar Diagnostic Interface Box (IFBOX)





Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.